Light Distribution Patterns and Types For Area Lighting June 26, 2024 – Posted in: Commercial Lighting, Lighting Information

Choosing the right light distribution pattern for area lighting can be a real head-scratcher. We’ve all been there, staring at lighting options and wondering which way to go. It’s no small decision – getting it right can make or break your space’s ambiance and functionality.
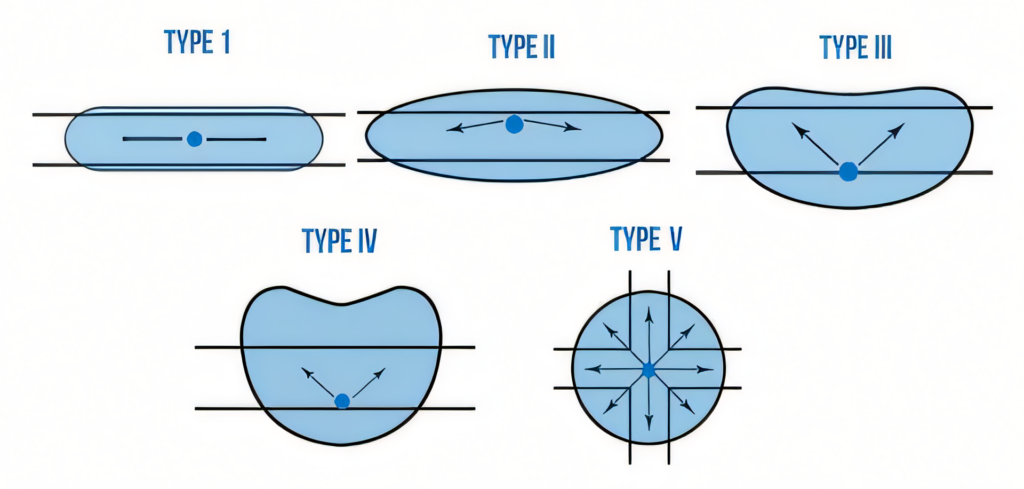
Luckily, the Illuminating Engineering Society of North America or IES has our backs. They’ve broken down light distribution into five handy types, taking some of the guesswork out of the equation.
In this article, we’ll walk you through these types and help you figure out which one fits your needs like a glove. So, ready to shine a light on this tricky topic?
Key Points
- Light distribution patterns for area lighting are divided into five types (I-V) by the Illuminating Engineering Society of North America.
- Type I is best for narrow areas like walkways, Type II works well for bike paths and narrow roads, Type III is ideal for wider roads and parking lots, Type IV suits building perimeters, and Type V provides 360-degree coverage for large open spaces.
- Choosing the right light distribution pattern depends on factors like space dimensions, intended use, and desired illumination levels to ensure proper visibility and safety.
- Proper light distribution enhances safety by reducing dark spots and glare, deterring crime, and creating a more secure environment for pedestrians and drivers.
- Different settings require specific light distribution patterns – for example, Type V is often used in parking lots and industrial areas, while Type II or III with lower intensity is preferred in residential settings.
Overview of Area Light Distribution Types
| Pattern | Description | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | Narrow distribution, suited for walkways | Narrow sidewalks, paths |
| Type II | Slightly wider than Type I, oval-shaped | Wider walkways, narrow roadways |
| Type III | Medium distribution, wider than long | Roadways, general parking areas |
| Type IV | Wide distribution, for mounting at perimeter | Wall-mounted area lighting, wide roads |
| Type V | Circular distribution, equal in all directions | Open areas, intersections, squares |
| Type VS | Square distribution | Parking lots, open areas |
Area light distribution types determine how illumination spreads across a space. These patterns range from narrow beams to wide, circular spreads, each serving specific lighting needs in various environments.
Type I Light Distribution
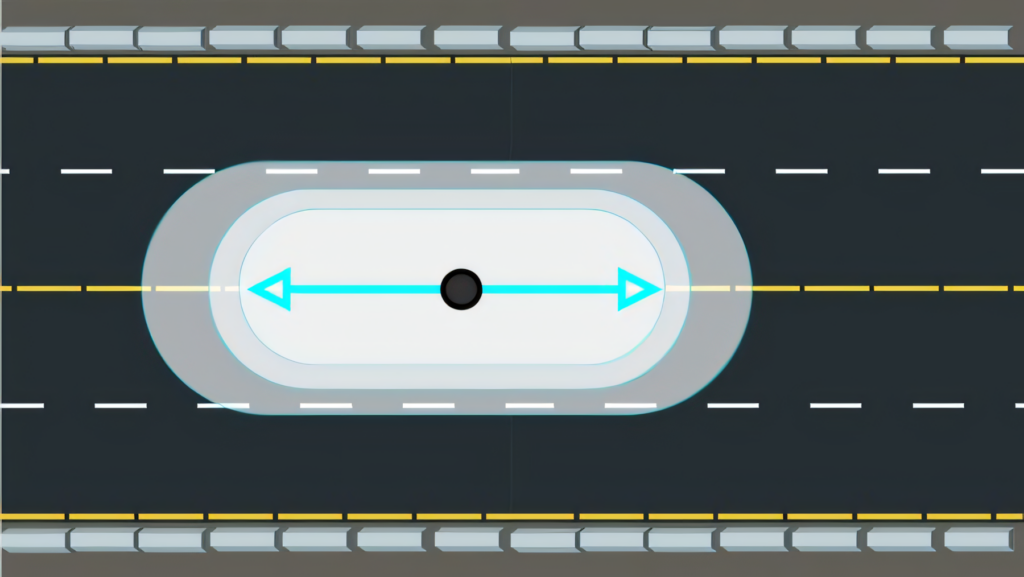
Type I light distribution is the narrowest pattern among outdoor lighting options. We often see this distribution used for walkways, paths, and roadway median lighting. It projects light forward in a long, narrow oval shape, with minimal light spreading to the sides.
The beam typically extends two to three times the mounting height in front of the fixture and about half the mounting height to each side.
Type I distribution illuminates long, narrow areas with precision and efficiency.
We’ve found that Type I fixtures work best when mounted directly above the area they’re lighting. This distribution excels at providing focused illumination without light trespass into surrounding areas.
For example, in a park setting, Type I lights can effectively illuminate walking paths without disturbing nearby natural habitats or residential areas.
Type II Light Distribution
We often encounter Type II light distribution in outdoor lighting designs. This pattern is characterized by its oval shape, extending twice as far along the street as it does across it.
It’s commonly used for narrower roadways, bike paths, and walkways where a more focused illumination is needed. Type II fixtures typically cast light 2.75 times wider than the mounting height, making them ideal for areas that require a concentrated beam of light.
In our experience, Type II distribution excels in scenarios where lighting needs to be placed on one side of a street or path. It provides a two-way lateral distribution, allowing the light to project outward and cover a specific area effectively.
This distribution type is particularly useful for illuminating long, narrow spaces without causing excessive light spillage into surrounding areas. We find this type of lighting mostly on smaller side streets, park pathways, and other areas where a concentrated light pattern is essential for safety and visibility.
Type III Light Distribution
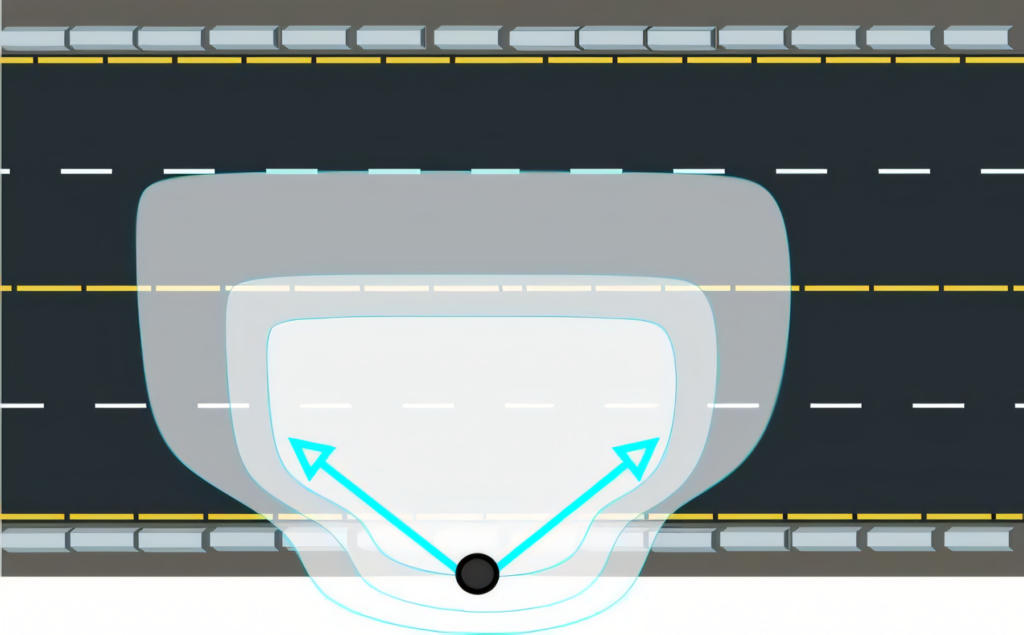
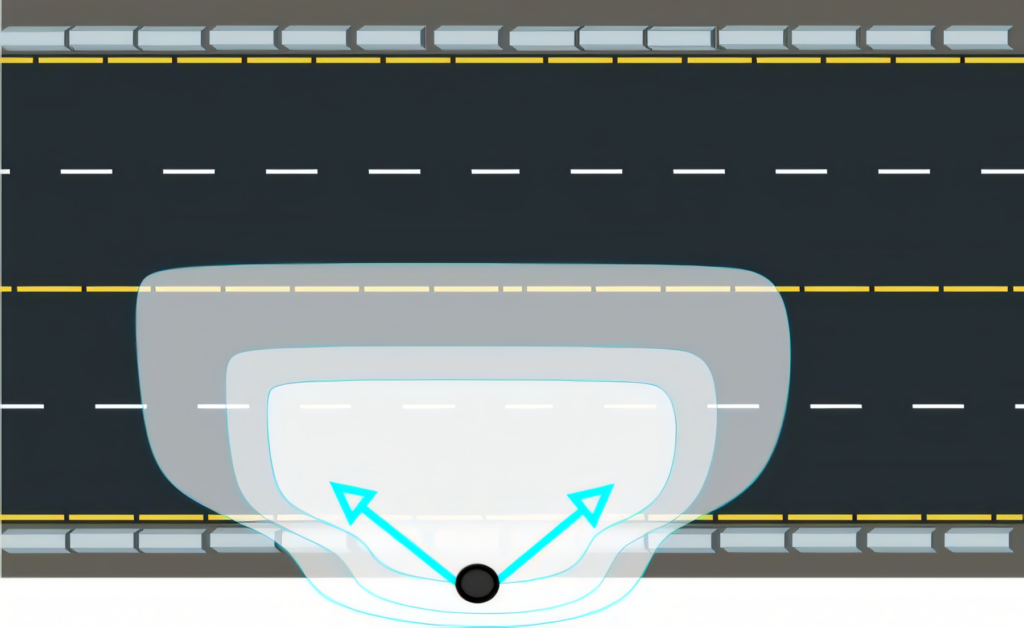
Type III light distribution is a popular choice for roadway and street lighting. This pattern casts light in a forward-throwing, asymmetrical shape, ideal for illuminating wider areas.
We see Type III fixtures often mounted on the side of roads, parking lots, and walkways. They efficiently distribute light forward and to the sides, covering a broader area than Type I or II distributions.

Our LED area lights with Type III distribution offer excellent coverage for medium to wide roadways. The light is dispersed at a 75-degree angle from the pole, providing uniform illumination across the target area.
This distribution type balances forward throw and lateral spread, making it versatile for various outdoor applications. Type III fixtures help minimize light trespass while maximizing visibility and safety in public spaces.
Type IV Light Distribution
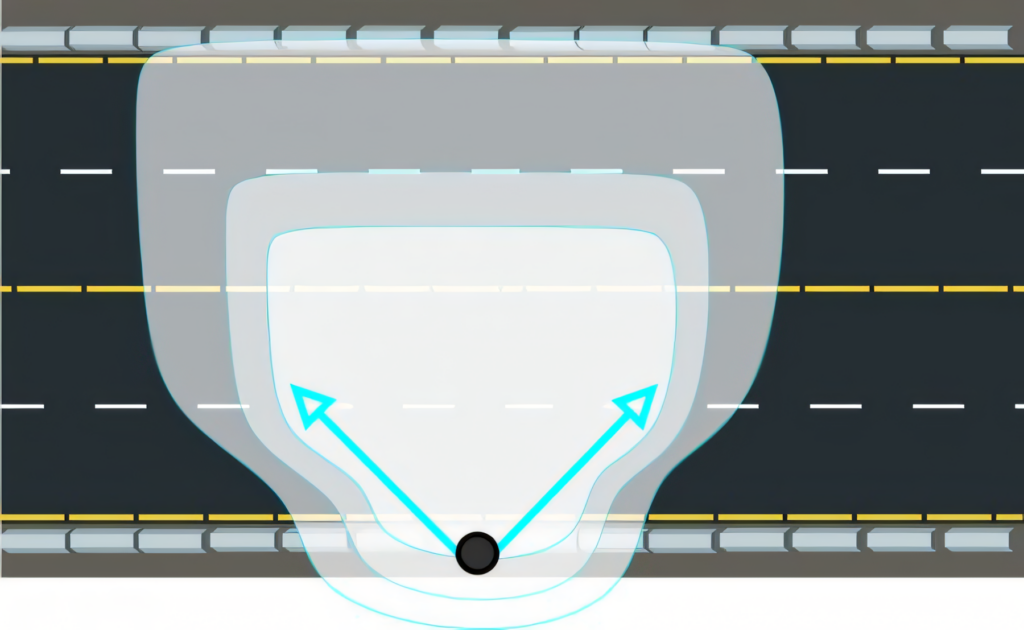
Type IV light distribution offers a wide, asymmetrical pattern ideal for perimeter lighting and large areas. We often use this distribution for parking lots, wide walkways, and building perimeters.
It casts light in four directions, creating a square-shaped illumination area that’s broader than it is deep.
Type IV distribution produces a semicircular light meant for mounting at or near the sides of buildings or areas.
This pattern pushes light outward and sideways, providing excellent coverage for areas that require uniform illumination across a wide space. The IESNA categorizes Type IV as part of its standardized approach to outdoor lighting design, helping professionals choose the right fixture for specific outdoor environments.
Type V Light Distribution
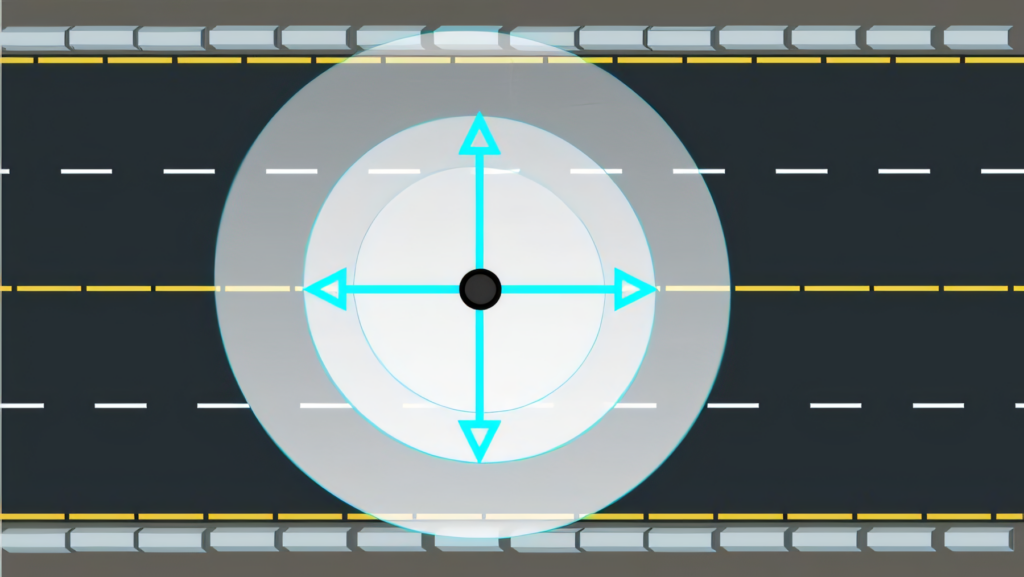
Type V light distribution offers a circular or square symmetry, providing equal illumination in all directions. We often use this pattern for larger areas where uniform lighting is essential, such as parking lots or open spaces.
It produces a 360-degree distribution with consistent light intensity at all positions around the fixture. This type of distribution is ideal for mounting fixtures at or near the center of roadways, intersections, or areas where a wide, even spread of light is needed.
We find Type V distribution particularly useful in scenarios requiring broad coverage without a preferred lateral direction. The circular symmetry version creates a cone-shaped area of light directly below the fixture, while the square symmetry option produces a more cube-like illumination pattern.
Both variations effectively light up expansive areas, making Type V an excellent choice for general area lighting in outdoor settings where visibility and safety are paramount.
Selecting the Appropriate Light Distribution Pattern

Choosing the right light distribution pattern is crucial for effective area lighting. We consider factors such as the space dimensions, intended use, and desired illumination levels to select the optimal pattern.
Considerations for Different Settings

We understand that selecting the right light distribution pattern is crucial for effective area lighting. Different settings require specific considerations to ensure optimal illumination, visibility, and safety.
- Roadway Lighting: Type II or Type III distributions are often ideal for roadways. These patterns provide wider coverage along the length of the road, illuminating both the street and sidewalks effectively.
- Parking Lot Lighting: Type V distribution is commonly used in parking lots. Its circular symmetry offers equal light distribution in all directions, covering a larger area efficiently.
- Walkways and Pathways: Type I distribution works well for narrow spaces like walkways. It concentrates light directly below and slightly forward, minimizing light spill into surrounding areas.
- Sports Fields: Type IV distribution is suitable for large open areas like sports fields. It produces a square 360° distribution, ensuring even coverage across the playing surface.
- Street Corners: A combination of Type II and Type III distributions can be effective at intersections. This setup provides adequate illumination for both the main road and side streets.
- Residential Areas: Type II or Type III distributions with lower intensity are often preferred in residential settings. These patterns balance visibility and minimize glare for homeowners.
- Commercial Districts: Type IV or Type V distributions are typically used in commercial areas. They offer wider coverage and higher intensity, suitable for busy shopping districts and plazas.
- Industrial Zones: Type V distribution is often chosen for industrial areas. Its circular pattern provides uniform illumination for large warehouse exteriors and loading docks.
Impact on Visibility and Safety

Proper light distribution significantly enhances visibility and safety in outdoor spaces. By selecting the right distribution pattern, we ensure adequate illumination across an area, reducing dark spots and glare.
This improved visibility helps prevent accidents, deters crime, and creates a more secure environment for pedestrians and drivers alike.
Different distribution types cater to specific needs. For instance, Type III LED light distribution is ideal for illuminating walkways and parking lots, while Type V produces a circular pattern perfect for open areas.
The right choice minimizes light pollution and maximizes energy efficiency, contributing to both safety and environmental responsibility. Our goal is to create well-lit spaces that protect people and property without unnecessary waste.
FAQs
What are the main types of light distribution patterns for area lighting?
The main types of light distribution patterns for area lighting are Type I to Type V. These patterns define how light is dispersed from LED fixtures. Each type is meant for different light needs and area sizes.
How does Type I light distribution work?
Type I light distribution has a narrow lighting pattern. It’s used where the light pattern needs to be focused. This distribution is great for lighting walkways or paths. The throw is taller than Type II and produces a more rounded distribution pattern.
What is the purpose of Type IV light distribution?
Type IV light distribution has a wider spread. It’s intended for areas where a larger area of lighting is required. This pattern pushes the light outward and is often used to light the side of an area or building.
How does Type V light distribution differ from other types?
Type V light distribution has a circular symmetry. It casts light in all directions, creating a 360° distribution that has equal light intensity at all positions. This type is used when lighting is required in all directions from the light source.
What factors should be considered when selecting the perfect light distribution?
When selecting the perfect light distribution, consider the width of the illumination area, the amount of light needed, and the specific light pattern needs. Also, think about glare and light pollution control.
How does NEMA beam spread relate to light distribution patterns?
NEMA beam spread is a system used to classify the lateral distribution of light fixtures. It helps in understanding how light fixtures will cast light. This information is crucial for choosing the right distribution type for LED area lighting needs.
I have been the project manager for Modern.Place since early 2016, spending three of those years working overseas on the manufacturing & procurement side of the LED lighting industry. Constantly learning and passing on knowledge to others while excited for what the lighting industry will involve into next.