Understanding Unified Glare Rating (UGR) July 25, 2023 – Posted in: Lighting Information, Office Lighting

Table of Contents
Introduction to UGR In Lighting
UGR, or Unified Glare Rating is a critical component in the field of lighting design. As lighting tech has advanced throughout the years, so to has the need to measure and manage visual discomfort caused by glare. UGR has become an important parameter and has even made it in European and Australian standards.
Key Takeaways
- UGR19 stands for a Unified Glare Rating of 19 or less. It’s a measure of glare used by lighting designers to quantify discomfort glare caused by bright light sources.
- The unified glare rating system measures direct light to predict “distraction levels” in a room. It averages the light values over surfaces like walls and work desks.
- Meeting these requirements ensures efficient lighting applications. This leads to better eye comfort and less disability glare. At the same time, it enhances safety levels and boosts the productivity of the occupants.
- To get a UGR19 rating, the designer needs to think about where to place the lights, which style to choose, how much light they give off, and how bright they are.
- The luminaire itself can’t be UGR19 compliant as the rating is determined by the physical space it’s installed in.

What is UGR19?
UGR19 stands for Unified Glare Rating of 19 or less and is a parameter that measures the brightness of a fixture in certain sample room layouts. This measurement matters a lot in workplaces where workers spend a lot of time daily on computers. Too high of a UGR rating might cause issues with productivity and eye strain, so most office spaces are encouraged to aim for a rating of 19 or below.
The UGR glare index ranges from 5 to 40, with a unified glare rating of 19 or less being the guideline for office spaces and classrooms. This is according to the Society of Light and Lighting.

These ratings assist in making spaces energy-saving and comfortable for everyone present. In addition, achieving UGR19 helps ensure that lights don’t exceed certain glare. This helps reduce light pollution level as well as user fatigue, headaches and eye strain.
Glare Index and UGR Table Comparison
This table compares British Glare Index (BGI), Visual Comfort Probability (VCP), CIE Glare Index (CGI), Daylight Glare Index (DGI), and Unified Glare Index (UGR).
| Glare sensation | BGI | VCP | CGI | DGI | UGR |
| Intolerable | 31 | 12 | 34 | 30 | 34 |
| Just intolerable | 28 | 20 | 31 | 28 | 31 |
| Uncomfortable | 25 | 28 | 28 | 26 | 28 |
| Just uncomfortable | 22 | 36 | 25 | 24 | 25 |
| Unacceptable | 19 | 43 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Just acceptable | 16 | 50 | 19 | 20 | 19 |
| Perceptible | 13 | 59 | 16 | 18 | 16 |
| Just perceptible | 10 | 67 | 13 | 16 | 13 |
| Imperceptible | 7 | 75 | 10 | 14 | 10 |
Understanding Unified Glare Rating (UGR)
UGR is used to measure the amount of discomfort glare that can result from direct or reflected light. It distinguishes between discomfort glare and disability glare, with the latter being more intense.
Difference between discomfort glare and disability glare
Glare is an uncomfortable light phenomenon that affects visibility and visual comfort. However, there are two distinct types of glare – discomfort glare and disability glare.
Discomfort Glare occurs when a strong source of light distracts from what one is viewing, thus creating an unpleasant sensation but not impairing vision.
On the other hand, Disability Glare actually hinders vision due to intense brightness and can lead to difficulty seeing clearly or completely becoming blind momentarily.

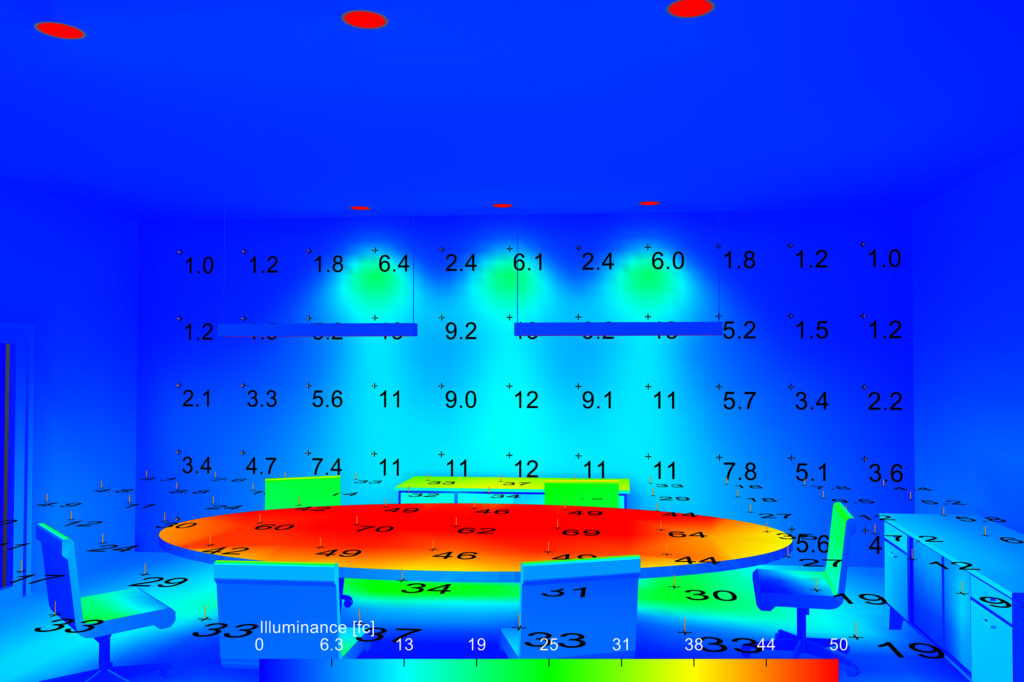
The UGR rating system measures how bright direct light sources are perceived by viewers and helps determine it if is acceptable or too distracting. There are three characteristics used to determine the level of distraction: luminance (the amount of reflected visible radiation), background luminescence (how present the surroundings appear) and total illuminance (overall illumination).
How UGR measures discomfort glare
UGR takes into account the direct light component in predicting discomfort glare due to its brightness and ‘risk index’, giving a numerical value as output determined via a mathematical formula.
When selecting fixtures, it’s important for designers and contractors to consider factors like size, shape, angle, and color temperature of lighting. These can result in varying ratings depending on how they affect perceived brightness and discomfort. For even better control, dimmable luminaires are also recommended.
UGR Formula & Calculation

UGR = 8 log [0.25/Lb * ∑ Ls2*ω/ρ2]
Examples of UGR ratings for different lighting scenarios
Knowing the UGR rating is particularly important for office spaces, as it helps to achieve the best lighting with the least amount of discomfort for the occupants that spend longer hours in a single space. This is part of the reason diffused panel lights and troffers have risen in popularity in recent years.

For instance, a single downlight with direct view from desk height may have an UGR rating ranging between 18-20 whereas a recessed office task light can have a lower range of 13-14 and a wall wash or linear indirect system having only up-lighting can reach much lower levels at 9-10.
Unified Glare Rating (UGR) Table By Application
| Type of area, task or activity (no. of sub-divisions) | Maximum UGR |
| Traffic zones inside buildings (4) | 25-28 |
| Rest, sanitation & first aid rooms (6) | 16-25 |
| Control rooms (2) | 19-25 |
| Store rooms & cold stores (2) | 25 |
| Storage rack areas (4) | 22 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Agriculture (4) | 25 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – bakeries (2) | 22 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Cement, cement goods (4) | 25-28 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Ceramics, tiles etc (7) | 16-28 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Chemical, plastic etc (8) | 16-28 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Electrical & electronics (6) | 16-25 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Foodstuffs, luxury food (8) | 16-25 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Foundries & casting (11) | 22-25 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Hairdressers (1) | 19 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Jewellery mfg. (4) | 16-19 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Laundries, dry cleaning (4) | 19-25 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Leather, leather goods (9) | 16-25 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Metal working (14) | 19-25 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Paper (3) | 22-25 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Power stations (5) | 16-28 |
| Printers (5) | 16-19 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Rolling mills, iron, steel (9) | 22-28 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Textiles (13) | 19-28 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Vehicles (6) | 19-22 |
| Industrial activities & crafts – Wood (9) | 19-28 |
| Offices (7) | 16-25 |
| Retail premises (3) | 19-22 |
| Places of public assembly, general areas (4) | 22-15 |
| Places of public assembly – Restaurants & hotels (7) | 19-25 |
| Places of public assembly – Theatres, cinemas etc (4) | 22 |
| Places of public assembly – Trade fairs & exhibitions (1) | 22 |
| Places of public assembly – Libraries (3) | 19 |
| Places of public assembly – Public car parks indoor (5) | 19-25 |
| Educational premises – Nursery school, play school (3) | 19-22 |
| Educational premises – Educational buildings (26) | 16-25 |
| Health care premises – Rooms for general use (8) | 22 |
| Health care premises – Staff rooms (2) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Wards, maternity wards (6) | 19-22 |
| Health care premises – Examination rooms (general) (2) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Eye examination rooms (2) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Ear examination rooms (2) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Scanner rooms (2) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Delivery rooms (2) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Treatment rooms (general) (6) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Operating areas (3) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Intensive care unit (4) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Dentists (4) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Laboratories & pharmacies (2) | 19 |
| Health care premises – Decontamination rooms (2) | 22 |
| Health care premises – Autopsy rooms & mortuaries (2) | 19 |
| Transportation areas – Airports (11) | 16-25 |
| Transportation areas – Railway installations (11) | 19-28 |
Challenges and Considerations of UGR19
UGR assessments involve complex calculations that consider the room’s physical characteristics, layout, fixtures, and accessories. This makes it challenging to fully meet the required standard without making extra changes or adjustments.

Additionally, lighting designs must also consider other factors such as aesthetics, energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness while also attempting to reach UGR19 and maintain office lighting standards.
As there can be many variables in creating a lighting solution, meeting all metrics for achieving UGR19 may prove difficult depending upon budget and available resources. In addition, human perception varies significantly from person to person.

Benefits of UGR19 in improving visual comfort
UGR has been proven to be an effective metric for measuring the level of discomfort glare in a variety of indoor environments. By helping lighting professionals identify potential sources of discomfort, UGR allows them to create lighting systems which benefit users by providing good visual comfort and improved productivity.
For example, schools can use UGR calculations when designing classrooms. This helps ensure students have good visibility with minimal eyestrain or distraction from excessive glare.

Similarly, healthcare facilities can use low glare fixtures that comply to ensure their patients are comfortably able to navigate the area as well as reducing errors due to poor visibility in staff areas.
Tips for choosing UGR19 Luminaires
Designers should aim for products and layouts that meet UGR<19 when calculating the UGR. Additionally, software such as DIALux can provide great direction on understanding this metric which can help determine the design needs for each space.
UGR VS Glare Rating Index
The Unified Glare Rating (UGR) and the Glare Index both measure glare in different ways. As discussed earlier, the UGR values are measured through calculations of light distribution to determine a numerical index for discomfort glare while the Glare Index is primarily focused on disability glare which involves impairment in vision due to bright sources and can be a result of reflected light from windows or glossy surfaces.

Basically, where UGR focuses on lumens emitted from fixtures, the Glare Index considers all types of light emissions from many surfaces – direct, indirect diffusion, etc. The combination of these two metrics allows lighting designers to determine efficacy levels and visual performance with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good UGR rating?
A UGR rating 19 or below is considered “Just Acceptable”, the lower the rating the better the result.
What does a low UGR mean?
A low UGR in lighting means there is low glare, which is a good thing. For offices, the recommended UGR rating is 16 to 19 to provide a comfortable work environment. Many office LED panels will display the rating directly on the box.
I have been the project manager for Modern.Place since early 2016, spending three of those years working overseas on the manufacturing & procurement side of the LED lighting industry. Constantly learning and passing on knowledge to others while excited for what the lighting industry will involve into next.